Anemia is a blood disorder that occurs when the body does not have enough red blood cells (RBCs), a common type of blood cell that is responsible for delivering oxygen around the body.
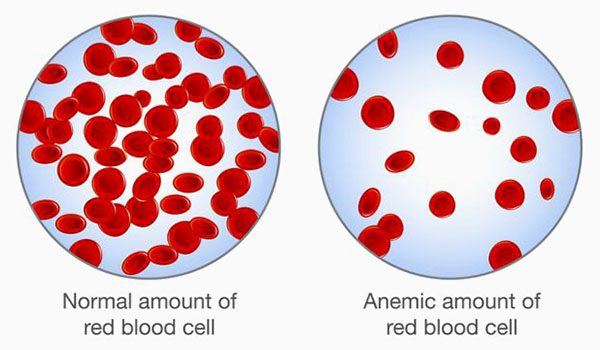
When you don’t have enough RBCs or the level of hemoglobin in your blood is low, your body doesn’t get the oxygen it needs. As a result, you may feel tired or have other symptoms.
Anemia is the most prevalent blood condition in the United States, affecting more than 3 million Americans. It can range from mild to severe. Although many anemia cases are mild and easily treated, some forms are severe and can even be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated appropriately.
What Causes Anemia?
There are three main causes of anemia:
1. Blood loss
Blood loss is the most common cause of anemia, particularly iron-deficiency anemia. It may occur due to heavy menstrual bleeding, hemorrhoids, stomach ulcers, surgery, trauma, or colon cancer.
2. Decreased RBC production
Your body may not produce enough red blood cells if your diet is lack in nutrients like iron, vitamin B12 and folate, or is not able to absorb these nutrients properly from the gut.
Problems with bone marrow may also cause decreased production of red blood cells. Aplastic anemia, for example, occurs when the bone marrow produces too few red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. It is a type of bone marrow failure.
Other causes include:
- Inherited conditions such as sickle cell anemia
- Pregnancy
- Chronic diseases, such as kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, leukemia and other blood cancers
3. Excessive RBC destruction
Anemia may also result when too many red blood cells are damaged or destroyed. Normally, red blood cells have a life span of 120 days in the bloodstream, but the body may destroy them before they complete their natural life cycle. This may occur when the immune system mistakes RBCs for a foreign substance and attacks them.
Other causes of an excessive RBCs destruction include:
- Infections
- Severe hypertension
- Blood clotting disorders
- Toxins produced by advanced kidney or liver disease
- Certain drugs, including some antibiotics
What are the Risk Factors of Anemia?
Factors that increase your risk for anemia include:
- Having a diet low in iron, folate, and vitamin B12
- Being pregnant and giving birth
- Having an intestinal disorder that affects the absorption of nutrients, such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease
- Having a chronic disease, such as AIDS, cancer, kidney disease, liver disease, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Having a family history of inherited anemia, such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia
- Excessive bleeding, due to trauma, surgery or childbirth
- Regularly taking medications that inflame the stomach lining, such as ibuprofen



